Blog
 2025-09-12
2025-09-12Nigeria, the world's largest cassava producer. The recent imposition of 14% tariffs by the United States on imports on Nigeria, bring both challenges and opportunities to its cassava processing industry. This article explores the multifaceted impact of these tariffs on Nigeria's cassava processing industry, drawing on economic analyses and industry insights.
 Nigeria cassava processing industry
Nigeria cassava processing industry
Which Impacts The U.S. High tariffs Will Have on Nigeria’s Cassava Processing Industry?
Although Nigeria's cassava processing industry has historically focused on domestic consumption and regional trade, The U.S. high tariffs could directly hinder its aspirations to expand into global markets.
Reducing Competitiveness: Higher tariffs make Nigerian cassava products, such as starch, flour, and processed foods, more expensive in the U.S. market, diminishing their competitiveness compared to suppliers from Southeast Asia or Latin America.
 cassava products
cassava products
Disrupting Value Chain Development: The cassava processing industry requires investment in infrastructure, technology, and export-oriented production. Tariffs could deter foreign investment and slow down the development of value-added products like industrial starch, alcohol, and animal feed.
What Opportunities Nigeria’s Cassava Processing Industry Will Meet Under the High Tariff?
Despite these challenges, the U.S. tariffs may accelerate Nigeria's efforts to boost domestic processing and diversify its trade partnerships.
 improving cassava varieties
improving cassava varieties
Import Substitution Policies: Nigeria has already implemented policies to promote cassava-based products, such as mandating the inclusion of 10% cassava flour in bread production. This reduces reliance on wheat imports and stimulates domestic cassava processing.
Export Market Diversification: Nigeria can leverage partnerships with China, the EU, and regional markets like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) to offset reduced access to the U.S. market.
What Can Nigeria Do to Stabilize its Cassava Processing Industry Under the High Tariff?
To mitigate the impact of U.S. tariffs, Nigeria's cassava processing industry must address inherent weaknesses, such as, limited value addition, low productivity and poor infrastructure, to stabilize its healthy development.
Increase Cassava Value Addition: Most processing focuses on products like garri and chips rather than higher-value items like flour, starch or bioethanol. For further value addition, Nigeria can introduce advanced technologies like cassava starch processing technologies to extend the production chain, boosting revenue.
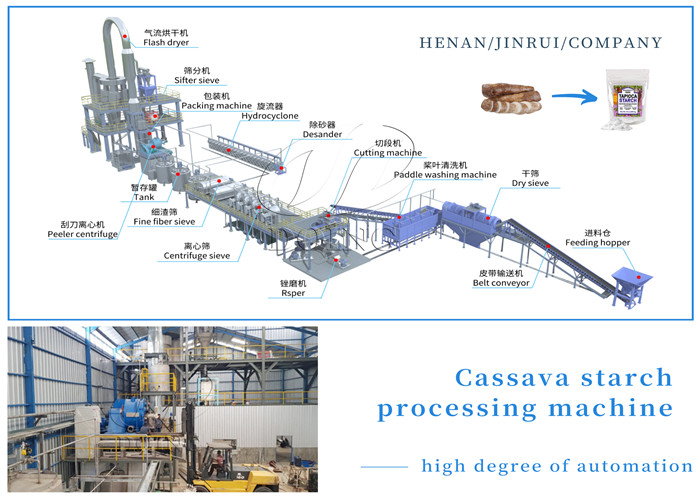 cassava starch processing
cassava starch processing
Enhance Cassava Productivity: Nigeria's cassava yields per hectare (10.6–15 tons) lag behind countries like India and Malaysia due to inadequate storage and processing facilities. Improving cassava storage facilities and processing technologies will reduce post-harvest loss and enhance productivity. Also, improving cassava varieties is available to increase yield from the source.
Other measures:
Strengthen Trade Alliances: Engaging with BRICS nations and other emerging economies can open new markets for Nigerian cassava products.
Enhance Regional Integration: By leveraging AfCFTA, Nigeria can access larger regional markets for cassava products, reducing reliance on extra-African trade.
The U.S. high tariffs pose significant challenges for Nigeria's cassava processing industry, but they also create an impetus for diversification and innovation. Wanna learn more about cassava processing information? Please focus Henan Jinrui! We aim to provide the latest industry news and suitable solution to every friends interested in cassava processing business!
Want to know more about our products or services? Fill out the contact form below, and we’ll to get back to you and you will get the price list. Please also feel free to contact us by email or phone.( * Denotes a required field).